Ever wondered how scientists achieve such precise measurements in their experiments or how medications are consistently produced with exact specifications? Behind these accuracies is a simple yet profound tool in the scientific world: the volumetric flask.
Volumetric flasks are a mainstay in laboratories worldwide, known for their precision in measuring liquid volumes and preparing solutions. Their unique design and calibration ensure that experiments and formulations are carried out with the utmost accuracy, which is crucial in research and industrial applications.
Here’s why they continue to be relevant and revolutionary in modern laboratories.

Overview of Volumetric Flasks in Laboratory Use
A volumetric flask is a type of glassware commonly used in laboratories, primarily for accurately measuring liquid volumes and preparing solutions of specific concentrations. Characterized by its long neck and pear-shaped bottom, these flasks come marked with a calibration line and are typically found in clear or amber glass. They are available in various sizes including 5ml, 10ml, 25ml, 50ml, 100ml, 250ml, 500ml, 1000ml, 2000ml, and 5000ml.
Why Are Volumetric Flasks So Crucial
Volumetric flasks aren’t just any glassware; they are precision tools designed for specific tasks. Accuracy and precision are paramount in the scientific world, and volumetric flasks are tailored to meet these requirements with their long neck and single graduation mark. They are used for diluting solutions to a known volume and are essential in preparing standard solutions for titration, among other uses.

Volumetric Flasks: Applications and Uses in Laboratory Settings
The primary purpose of volumetric flasks is to dilute solutions, prepare solutions, and prepare sample solutions. They allow precise measurement of specific volumes of liquids and are crucial for creating solutions of different concentrations to meet the needs of experiments or industrial production. Additionally, volumetric flasks are used in preparing sample solutions for chemical analysis or physical testing.
Here’s how volumetric flasks are commonly used:
- Measuring Liquid Volume: Volumetric flasks have calibration lines for direct volume reading. They are used to measure liquid reagents’ volumes in experiments, especially for precise dilutions and quantitative transfers.
- Preparing Solutions: These flasks are often used to prepare standard solutions and accurate dilutions. By dissolving a solid solute in a suitable solvent, a solution of a certain concentration is prepared. The high precision of volumetric flasks meets the demanding requirements of laboratory solution preparation.
- Storing Liquids: They can also be used to store liquid reagents or samples in experiments, preventing evaporation, contamination, or degradation.
- Other Uses: Volumetric flasks might be employed for preparing sample solutions, separating reactants and products, purifying substances, and determining reaction equilibrium constants in various experimental operations.
How Did Volumetric Flasks Change the Laboratory Landscape
Before the widespread adoption of volumetric flasks, there was a significant challenge in standardizing measurements across different scientific disciplines and countries. This lack of standardization was particularly problematic in chemistry and pharmacology, where precise measurements were crucial for experiments and drug formulations.
In the late 19th century, as the scientific community moved towards a more unified system of measurement, volumetric flasks played a critical role. They enabled chemists to prepare solutions with exact concentrations necessary for creating standard reference materials. One pivotal example is the standardization of the molar concentration, a fundamental unit in chemistry that expresses the concentration of a substance in a solution.
The introduction of volumetric flasks allowed for the accurate preparation of primary standard solutions, which are solutions with a precisely known concentration determined using a substance of known purity. These primary standards became the basis for calibrating other measurement devices and for conducting various critical chemical analyses, including acidity or pH measurements, and complexometric titrations used in metal ion determinations.
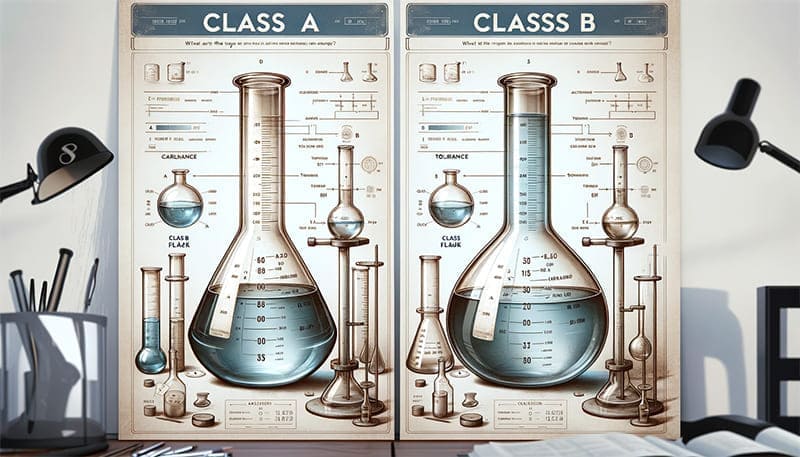
What Are The Types of Volumetric Flasks
Volumetric flasks come in various sizes, ranging from 1 mL to several liters, and typically two types: Class A and Class B. Class A flasks are designed for maximum accuracy and are used in high precision analytical work. Class B flasks are slightly less precise but still provide good accuracy for general laboratory work.
Here are the specific differences between Class A and Class B volumetric flasks presented in a table format:
| Feature | Class A Volumetric Flasks | Class B Volumetric Flasks |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Highest precision and accuracy. | Less precision and accuracy than Class A. |
| Tolerance | Lower tolerance, meaning the volume is closer to true value. | Higher tolerance, meaning more variation in volume. |
| Usage | Used in high precision analytical work and research. | Used for general laboratory work and teaching. |
| Certification | Often come with a certification of accuracy. | May or may not come with certification. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to higher precision. | Less expensive than Class A. |
| Calibration | Usually calibrated to contain (TC) or to deliver (TD). | Same as Class A, but with broader tolerances. |
| Label | Typically marked with a serial number and a label. | Less often marked with detailed information. |
Class A flasks are typically used in situations where precision is crucial, such as in quality control or research settings, while Class B flasks are more common in educational settings or for general laboratory work.
How Are Volumetric Flasks Used
The process of using a volumetric flask involves several steps to ensure accuracy: cleaning, filling to the mark with the liquid or solution, and then ensuring the liquid’s meniscus aligns precisely with the graduation mark. This process, although simple, requires a steady hand and a keen eye for detail.
Correct Usage of Volumetric Flasks
- Cleaning: Volumetric flasks should be cleaned before use with warm water and neutral detergent, followed by thorough rinsing. If needed, chromic acid cleaning solution might be used, followed by a thorough water rinse to avoid any residue that could affect the experiment.
- Checking for Leaks: Before using a volumetric flask, check for any leaks by filling it halfway with water, sealing it with a stopper, inverting it, and observing for any leakage.
- Preparing Reagents: Prepare the appropriate amount of reagent as required by the experiment. Ensure the reagents are at room temperature before transferring them into the volumetric flask.
- Transferring Solutions: Carefully transfer the prepared solution into the volumetric flask using a funnel or glass rod to guide the liquid, preventing it from touching the outer walls of the flask.
- Diluting to Mark: Continue adding solvent until the liquid level is about 1 cm below the calibration mark. Then, use a dropper to carefully add the last drops until the bottom of the meniscus touches the calibration line.
- Mixing: After sealing the flask, invert and shake it several times to ensure the contents are thoroughly mixed.
- Labeling: Once the solution is prepared, label the flask with the solution’s name, concentration, volume, and other relevant information.
When using volumetric flasks, it’s important to handle them carefully, avoid using them with hot liquids or storing large quantities of liquid reagents, and always label them properly to prevent mix-ups. Proper usage, regular maintenance, and careful storage are key to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experiments involving volumetric flasks.
Further Considerations When Using Volumetric Flasks
- Selection: Choose the appropriate size of the volumetric flask based on the volume of solution needed for your experiment. Ensure the flask’s volume suits the precision required.
- Avoid Overfilling: When filling the flask, ensure the liquid reaches just the calibration mark. Overfilling or underfilling can lead to inaccurate measurements.
- Minimizing Errors: When making up solutions, add the solute first, followed by a portion of the solvent. After the solute has dissolved, fill up to the calibration mark with the solvent. This sequence minimizes errors in concentration.
- Temperature Considerations: Be mindful of the temperature of the liquids and the flask itself. Volumetric flasks are calibrated at a specific temperature (usually 20°C), and significant temperature deviations can lead to volume errors due to expansion or contraction of the glass and the liquid.
- Handling and Storage: Handle the flask with care to prevent breakage or injury. Store them in a safe, upright position, and do not stack them as they are prone to tipping and breaking. Ensure they are thoroughly cleaned and dried before storing.
- Safety Precautions: Never use volumetric flasks for heating substances or for reactions that release gases, as they are not designed to withstand pressure or high temperatures. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection, when handling chemicals and glassware.
- Observation and Documentation: During the experiment, closely observe the reaction and any changes in the solution. Document all steps, concentrations, and volumes for future reference and reproducibility.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect volumetric flasks for etches, cracks, or chips, especially around the neck and calibration mark. Even minor damage can significantly affect the accuracy of the volume measurements.
By adhering to these guidelines, researchers and technicians can ensure precise and reliable use of volumetric flasks, contributing to the success and integrity of their scientific experiments. Proper technique and attention to detail are crucial in all laboratory settings, especially when working with precise instruments like volumetric flasks.

Key Points in Using Volumetric Flasks
When using volumetric flasks, cleanliness is paramount. Residue from previous contents can affect volume measurements. Additionally, when filling the flask, the temperature of the liquid should be considered as it can expand or contract with temperature changes, impacting volume.
Here are expanded details on the critical points to consider:
- Cleanliness is Paramount:
- Before Use: Always clean the flask with appropriate solvents to remove any previous residue. This might include rinsing with distilled water, followed by solvents like ethanol or acetone, and then a final rinse with distilled water.
- After Use: Clean immediately to prevent substances from drying and sticking, which can be harder to clean later and might affect future measurements.
- Temperature Considerations:
- Constant Temperature: Perform measurements at a constant temperature, preferably room temperature, to ensure consistency. Volumetric flasks are calibrated for a specific temperature (usually 20°C), and deviations can lead to errors.
- Avoid Extremes: Do not use the flask with extremely hot or cold liquids unless it is specifically designed to withstand such conditions. Sudden temperature changes can cause glass to crack or measurements to be inaccurate.
- Filling to the Mark:
- Use a Funnel: When adding liquids, use a clean funnel to avoid spillage on the neck, which can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Eye Level: Ensure the meniscus (the curve seen at the top of the liquid) aligns with the calibration mark at eye level to avoid parallax errors.
- Use a Dropper: For the final adjustment, use a dropper or pipette to add or remove liquid until the bottom of the meniscus is exactly at the mark.
- Mixing Solutions:
- Gentle Swirling: Once the flask is filled to the mark, stopper it and invert gently to mix the solution, ensuring a homogeneous mixture without vigorous shaking that might cause spills or lead to the formation of bubbles.
- Avoid Contamination:
- Don’t Overfill: Overfilling can lead to spills and contamination when stoppering or mixing.
- Use Clean Stopper: Always use the stopper that comes with the flask, ensuring it’s clean and fits properly to avoid evaporation and contamination.
- Storage and Handling:
- Proper Storage: Store volumetric flasks in a stable, upright position and in a place where they won’t be knocked over or exposed to contaminants.
- Handle with Care: Being made of glass, volumetric flasks are breakable. Handle them with care, using both hands when necessary, especially with larger flasks.
- Regular Calibration:
- Periodic Checks: Regularly check and, if necessary, recalibrate your flasks, especially if they are used frequently or used for high-precision measurements.
By following these detailed practices, you can ensure the accuracy and reliability of your measurements, as well as the longevity of your volumetric flasks. These practices are crucial in maintaining the rigorous standards expected in scientific research and various industrial applications.

FAQs on Volumetric Flasks
What is a volumetric flask and how is it used?
A volumetric flask is a type of lab glassware known for its precise volume measurements. It’s primarily used in preparing standard solutions and diluting liquids accurately within laboratories.
How do you clean a volumetric flask?
Clean a volumetric flask with distilled water followed by appropriate laboratory detergents. Rinse thoroughly with distilled water, and ensure it’s dry before use. For stubborn residues, specific cleaning agents like chromic acid may be used, followed by thorough rinsing.
What’s the difference between Class A and Class B volumetric flasks?
Class A flasks offer higher accuracy and lower tolerances, making them suitable for high-precision analytical work. Class B flasks are less precise and more suited for general laboratory tasks or educational purposes.
Can volumetric flasks be used for heating liquids?
Generally, volumetric flasks are not designed for heating. They are made of glass that could crack or break with sudden temperature changes. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines before applying heat.
How do you ensure accurate measurements with a volumetric flask?
To ensure accuracy, fill the flask to the calibration mark at eye level. The bottom of the meniscus (the curve of the liquid) should align with the mark. Use distilled water at a known temperature, typically around 20°C, as volumetric flasks are calibrated for specific temperatures.
Where can I find high-quality volumetric flasks?
High-quality volumetric flasks are available at specialized laboratory equipment suppliers. You can browse our selection of premium volumetric flasks at Glasswaree.
Conclusion
In exploring the pivotal role of volumetric flasks in modern laboratories, we’ve unveiled their precision, versatility, and enduring relevance. Whether for high-stakes research or routine tasks, understanding and utilizing volumetric flasks is crucial for any scientific endeavor. Continue your journey in scientific precision and explore an array of volumetric flasks suited for your every need at Glasswaree. Embrace accuracy today for a clearer tomorrow in your scientific explorations!










